ENTERPRISE SECURITY IN THE CONNECTED WORLD USING BIOMETRICS
Today the work lifestyle has changed. Advances in mobility and connectivity have accelerated the evolution of the modern business, allowing new types of enterprises to emerge. Thanks to the Covid-19 kind of situation and cheaper gadgets with good data connectivity, nine to-five workdays confined to the cubicles of an office space is no longer the norm.
Wireless technology enables remote workers and mobile offices, keeping businesses on the move and allowing them to span the world. And while this new kind of work opens up innovative new opportunities, it also brings with its new security challenges, specifically in regard to access management and fraud prevention.
The new challenges of today’s mobile-enabled workplace stem from an identity crisis. With so many different access points to a business, it is more important than ever to have assurance that persons granted permission onto an enterprise’s network are who they claim to be, regardless of the passwords they know or the security keys they have.
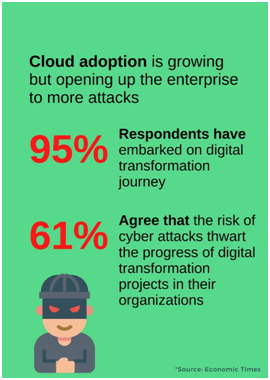
The consequences of this workplace identity crisis are plastered across today’s headline. A CIO survey by Forcepoint and Frost & Sullivan found that 69% of Indian organisations are at risk of data breach, with 44% of them encountering a data breach before and 25% failing to perform any breach assessment in the last 12 months. It also found that not enough C-level teams are involved in cyber security preparations, with only 34%, mainly at BFSI, telecom and IT & BPO companies, involved in it. India suffers the second highest number of cyber-attacks, and the average cost of data breach rose by 8% in 2018-19 compared to last year.

IT companies and financial Institutions are top buyers of Cyber Insurance with premium varying from 4.5 lacs to 8 crore a year. Other buyers of cyber insurance are companies from Pharma, retail, hospitality as also R&D and IP based organisations.
Identity lies at the heart of security, and so strong identity technologies have emerged in lockstep with the rise in connected world. They enable enterprises to better safeguard the sensitive assets upon which they rely to be competitive. At the forefront of these technologies is biometric authentication. Flexible, secure, and intuitive… done right, biometrics can solve the identity crisis of today’s mobile workplace, enhancing security, efficiency, and convenience.
Biometric Authentication in the Connected world
Authentication is the process of proving to a system that you are who you say you are. Traditionally, this has been done with passwords and usernames. Passwords may have been sufficient before the advent of networks that allow for remote access to databases, but time has proven they are no longer sufficient for enterprise security. Most of the data breaches are the result of compromised password credentials that impostors used to authenticate.
The inadequacy of the password in the age of remote computing is easy to understand. Because a password is a piece of information, presenting it to authenticate only proves one thing: you know the password. A password system does not protect against stolen passwords, guessed passwords, or phished passwords. And what is more, they are inconvenient for the demands of connected culture.
Biometrics technology makes use of measurements of a user’s unique behaviours and physical traits. Your fingerprint, your iris, the sound of your voice, these are all aspects of your biological identity that no one else has. Biometric technology essentially leverages these traits as a digital proxy of identity to prove you are who you claim to be to an information system. This makes biometrics ideal for authentication
In an authentication scenario, biometrics can fully replace passwords. To login to a workstation or gain access to an account, a user simply scans their biometric – by placing their finger on a fingerprint sensor, for example, – and the measurements from the scan are compared to a biometric template associated with the authorized user. If the biometric submitted matches the information in the template, and is proven to be from a live person, access is granted. If not, it’s denied. The proposition is simple, secure, and convenient.
Benefits of Biometric Authentication.
The benefits of biometric authentication in the workplace are myriad. From a security standpoint, biometrics are largely immune to the pitfalls of passwords. This is because biometrics are not secreting, and so they cannot be shared, lost, or phished. Their security is based upon their difficulty to reproduce.
Beyond increased security, however, biometric authentication also brings greater convenience and efficiency to the next generation enterprise. With biometrics, workers never lose or forget their credentials, eliminating time-consuming password resets and credential reissuance. Once a user is on boarded in the hiring process, submitting to a one-time biometric enrolment, they are set for easy access with no risk of demanding more work from administrators. When an employee or contractor leaves a company for any reason, it is just as simple to revoke their access, re-securing company assets without having to worry about changing passwords.
Key considerations that need to be considered for Biometric Authentication
Presentation Attack Detection
To protect against fraudulent attacks targeting the biometric security features, biometric authentication mechanisms include functions to perform spoof detection
Replay Attack Detection
When the sensor acquires a raw biometric data, it sends the raw data to feature extractor Module for pre-processing through a communication channel. This channel is in between the sensor and the feature extractor module. It is intercepted to steal the biometric trait and store somewhere else. The previously stored biometric trait is replayed to the feature extractor to bypass the sensor.
Tampering the Database
This occurs when the imposter compromises with the security of the database by adding new templates, modifying existing templates and removing existing templates. It is not an easy task to attack the system database.
To prevent such attacks the solution should have a strong encryption at the time of enrolment with key generation mechanism
Key generation: In this the helper data is obtained from the biometric traits and the cryptographic key is directly generated from the helper data
Key release: In this helper data is obtained by binding a key with biometric template
Implementing Biometric Solution
Precision has developed a holistic solution suite comprising of biometric hardware and software modules that can suit all common usage scenarios across industry segments. The modular design of the InnaIT™ framework provides flexibility – the organization may choose the specific modules that are needed and expand as the user base grows. The solution not only provides authentication, the algorithm detects authentication spoof, replay attacks and database attacks.
The InnaIT™ framework also simplifies the implementation – eliminating the need for complex integration of multiple security solutions. Additionally, the entire solution is provided by one solution provider, Precision Biometric, so you do not have to coordinate with multiple vendors.
The attributions for the blog are:
- Aware.com, Enterprise Security in the Age of Remote and Mobile Work
- Economic Times, 69% Indian companies at risk of data breach
- Times of India, Average data breach cost in India up by 8%
- Norton.com, Biometrics and Biometric data: what is it and is it secure?